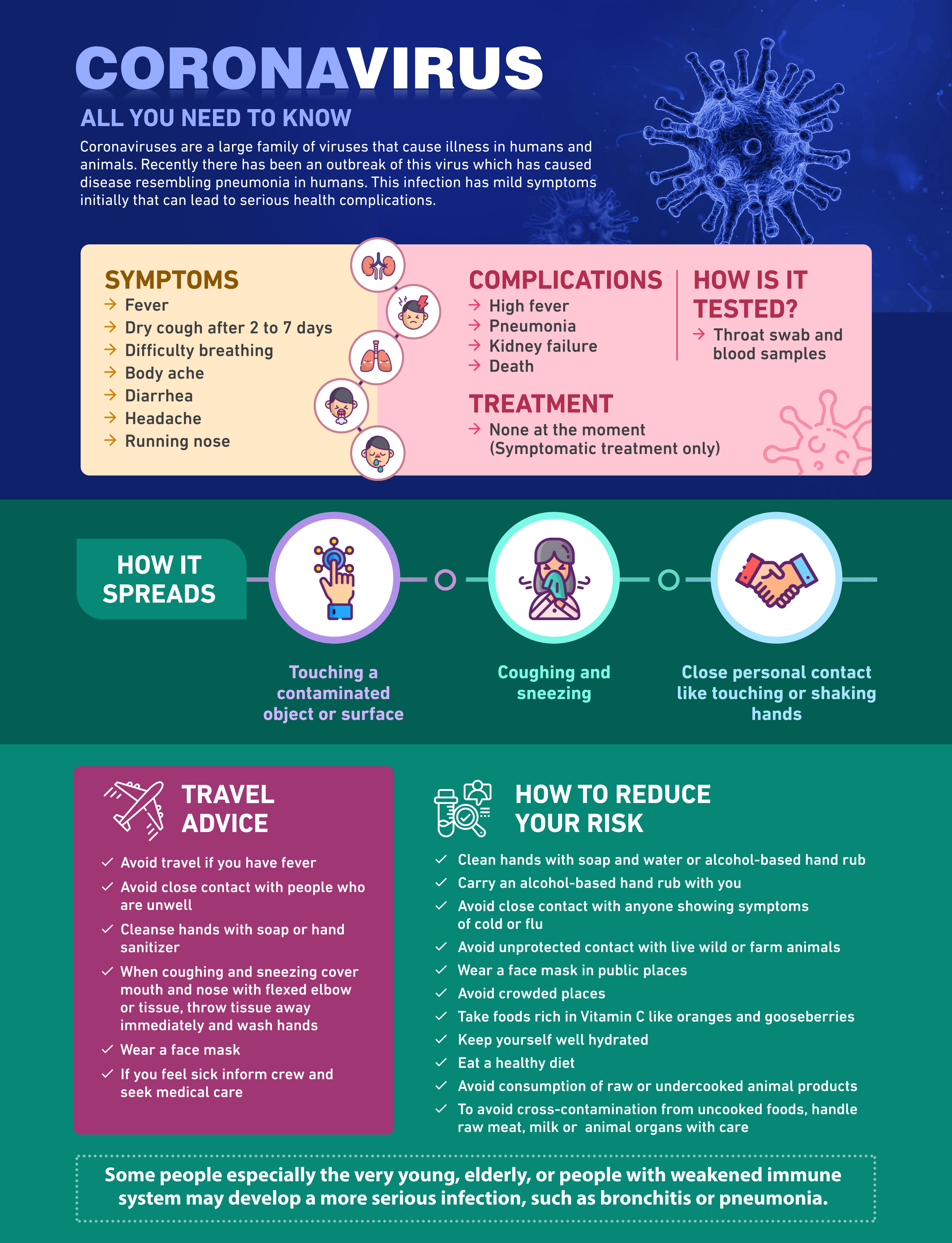
Does Vitra offers Covid 19 Test?
Yes! We offer Covid 19 test
- SARS Cov 2 Antibodies Test
- SARS Cov 2 Antigen Test
- RT-PCR test for Covid 19
- SARS Cov2 IgG (Elisa)
- SARS Cov2 IgM (Elisa)
All test are done after doctors prescriptions under our trend technician and Doctors.
What is an Antibody Test?The body immune system produces antibodies - proteins that are critical for fighting and clearing out the virus.
Introduction: SARS CoV 2 is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus of the family Coronaviridae, genus Beta coronaviruses.
SARS CoV 2 is transmitted person-to-person primarily via respiratory droplets, but also indirect transmission through contaminated surfaces is possible.
SARS CoV 2 can be isolated from respiratory samples obtained via naso/oropharyngeal swabs or from sputum. The virus accesses host cells via the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), which is the most abundant in the lungs.
The incubation period for COVID 19 is thought to range from 2-14 days following exposure, with most cases showing symptoms approximately 4-5 days after exposure.
Definite COVID 19 diagnosis entails SARS CoV 2 detection by RT PCR method
Antibody to SARS CoV 2 is an immunoassay test for qualitative detection of antibodies (including IgG) to Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV 2).
Seroconversion or recovery is observed after a median of 10-13 days after symptom onset for IgM and 12-14 days for IgG and last for several months. Levels and chronological order of IgM and IgG antibody appearance are highly variable supporting detection of both antibodies simultaneously.
How Does an Antibody test work?Antibody testing, also known as serology testing, is done after full recovery from COVID-19. Eligibility may vary, depending on the availability of tests. A health care professional takes a blood sample, usually by drawing blood from a vein in the arm. Then the sample is tested to determine whether you'sve developed antibodies against the virus.
What is the difference between a Coronavirus test and antibodies test?Covid RT PCR Nasopharyngeal swab test is definite diagnosis for SARS CoV 2 infection. The FDA approved two types of tests for diagnosing COVID-19 - molecular and antigen.
- Molecular test- This test detects genetic material of the virus using a lab technique called polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Also called a PCR test, a health care worker collects fluid from a nasal or throat swab or from saliva. Molecular tests are considered very accurate when properly performed by a health care professional
- Antigen test- This newer COVID-19 test detects certain proteins that are part of the virus.
Using a nasal or throat swab to get a fluid sample, antigen tests can produce results in
minutes. Because these tests are faster and less expensive than molecular tests are, some
experts consider antigen tests more practical to use for large numbers of people. A positive
antigen test result is considered very accurate, but there's an increased chance of false
negative results - meaning it's possible to be infected with the virus but have negative
antigen test results. So antigen tests aren't as sensitive as molecular tests are. Depending
on the situation, the doctor may recommend a molecular test to confirm a negative antigen
test result.
Antibody test helps to find recovery or seroconversion from the virus and done 2 weeks post symptoms. - The timing and type of antibody test affects accuracy. so test ideally done after 2 weeks of infection
- Another benefit of accurate antibody testing is that people who've recovered from COVID-19 may be eligible to donate plasma, a part of their blood.
- Antibody tests results indicate how many people had COVID-19 and recovered, including those who didn't have symptoms. This aids in determining who might have immunity. It can also help in contact tracing to assess who else is at risk of infection and how far the disease spread. All of this data will help improve strategies to curb the COVID-19 pandemic.
- But the World Health Organization cautions that there's a lack of evidence on whether having antibodies means you're protected against re-infection with COVID-19. The level of immunity and how long immunity lasts are not yet known
